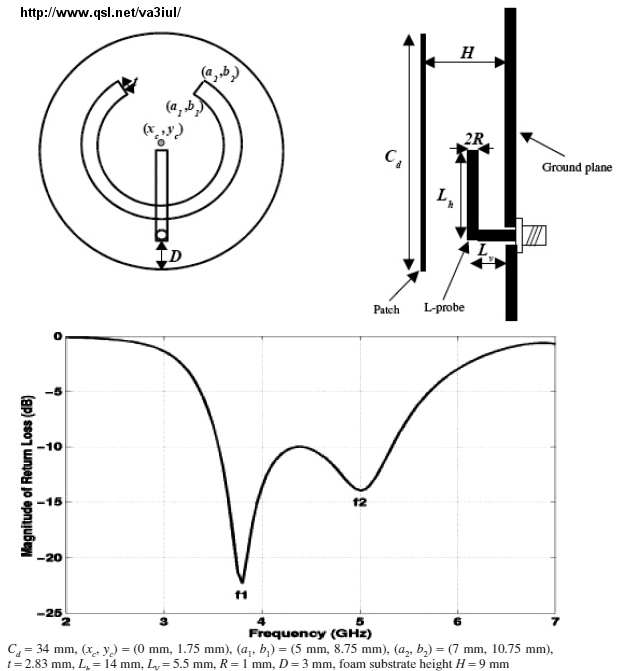
This paper presents performance of a coaxially feed L- shape microstrip patch antenna for WLAN application. The proposed antenna has been designed by etching L-shaped structure on a rectangular patch. In order to achieve the desired bandwidth, the.
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by a driving frequency, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in a way similar to a dipole antenna. The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving frequency, determine the radiation pattern. Often the radio waves are provided by a waveguide, and the antenna consists of slots in the waveguide. Slot antennas are usually used at UHF and microwave frequencies, where the waves are usually conducted by waveguide, so a slot in the waveguide makes a simple antenna. They are often found in standard desktop microwave sources used for research purposes. A slot antenna's main advantages are its size, design simplicity, and convenient adaptation to mass production using either waveguide or PC board technology.
An antenna consisting of multiple parallel slots in a waveguide is a widely used array antenna which radiates a narrow fan-shaped beam of microwaves at right angles to the waveguide, with its narrow axis in the plane of the waveguide and its wide axis perpendicular to the waveguide. Multiple slot versions are widely used in radar antennas, particularly marine radar antennas on ships, and for the sector antennas used for cell phone base stations.
Due to Babinet's principle a slot in a waveguide has the same radiation pattern as a driven rod antenna whose rod is the same shape as the slot. This can be used to determine the radiation pattern using calculations for a more conventional antenna.

The slot antenna was invented in 1938 by Alan Blumlein, while working for EMI. He invented it in order to produce a practical type of antenna for VHF television broadcasting that would have horizontal polarization, an omnidirectional horizontal radiation pattern and a narrow vertical radiation pattern.[1][2]
See also[edit]
- Microwave Radiometer (Juno) (has a slot array antenna)
- RIMFAX (radar for Mars rover has slot antenna design)
References[edit]
- ^Blumlein, Alan (1938-03-07), 'Improvements in or relating to high frequency electrical conductors or radiators', British patent no. 515684
- ^Burns, Russell (2000). The life and times of A.D. Blumlein. Institution of Engineering and Technology. ISBN0-85296-773-X.
Microstrip Antenna Hfss
External links[edit]
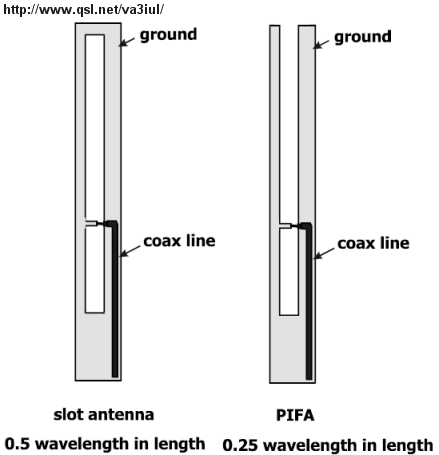
- 'Slot Antennas'. Antenna Theory.